This guide is mostly about getting tech help, but it also applies to getting clarifications on module topics too. e.g. what is the difference between refactoring and rewriting?

Keep in mind that instructors don't have ready solutions to all technical problems. Unlike tutorial questions for which instructors have model solutions, given the complexity of industry tools we use (Gradle, Travis, Git, ...) and the rapid pace they are updated, instructors don't have ready solutions to most technical problems you face in this module. The only realistic way to solve those problems at a large scale is crowd-sourcing i.e., someone else who faced a similar problem might know how to fix it.
What not to do:
- Send a help request to an instructor: When faced with a technical problem or a doubt about a concept, don't fire off an email lecturer/tutor immediately, unless it is something only the lecturer/tutor is supposed to know.
- Request to meet the instructor to solve the problem: That can only work if the person is supposed to know how to solve all technical problems, which is not the case.
What to do:
-
Double-check the given instructions: Often, technical problems arise due to deviations in how you perform a step or a difference in your environment.
-
Get your team to meet for a weekly work-together session. When you do module tasks together, it is easy to compare with each other and figure out what deviation is causing the problem. That is, crowd-source your team first.
-
Search: It is very likely the answer already exists somewhere in the cyberspace. Almost every programming-related question has been answered in places like stackoverflow. Don't give an opportunity for someone to ask you to STFW.
Pay attention to the error message you encounter. Sometimes it also contains hints as to how to fix the problem. Even if not, a web search on the error message is a good starting point.
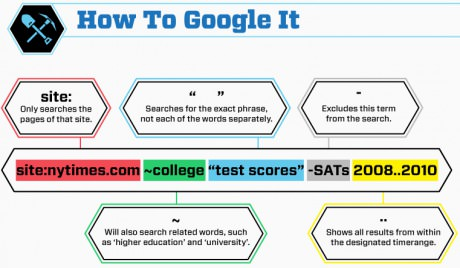
-
Ask in the module forum:
-
Give full details of the problem Conversations via online forums take time. If you post everything that is relevant to your problem, your chances of getting an answer in the first try is higher. If others have to ask you more questions before they can help you, it will take longer. But this doesn't mean you dump too much information into the thread either.
- Include full error message, screenshots, code snippets, stack traces, etc.
- If the problem is code-related, push the current state of the code to a branch in your fork and give the link to the branch. That gives a chance for someone to reproduce the state of your project in their computer.
- Include full error message, screenshots, code snippets, stack traces, etc.
-
Avoid addressing the question to one person (e.g., the prof), unless really necessary. Doing so will discourage others from answering that question.
-
Isolate the problem. "My code doesn't work" isn't going to help even if you post the whole code. Others don't have time to go through all of your code. Isolate the part that doesn't work and strip it down to the bare minimum that is enough reproduce the error. Sometimes, this process actually helps you to figure out the problem yourself (have you heard about Rubber Duck Debugging?).
How to isolate problematic code? Delete code (one bit at a time) that is confirmed as not related to the problem. Do that until you can still reproduce the problem with the least amount of code remaining.
-
Generalize the problem. "How to write tasks to a text file using Java" is too specific to what you are working on. You are more likely to find help if you post a thread called (or search for) "How to write to a file using Java".
-
Remember to thank those you try to help, and close the issue after the issue has been resolved.
-

Rubber duck debugging is an informal term used in software engineering to refer to a method of debugging code. The name is a reference to a story in the book The Pragmatic Programmer in which a programmer would carry around a rubber duck and debug his code by forcing himself to explain it, line-by-line, to the duck.
[for more, see wikipedia entry]
- Ask the world using programming forums such as stackoverflow.
-
PLEASE search for existing answers before you post your question in those public forums; You don't want to appear as a 'clueless' or 'too lazy to do your research' person in a public forum.
Know what these stand for: RTFM, STFW, GIYF
-
- Raise your question during a tutorial. Some questions can be discussed with the tutor and tutorial-mates.
What kind of questions are suitable to discuss with the tutor? Consider these two questions you might want to ask a tutor:
- Good This is how I understood/applied coupling. Is that correct? - Such questions are welcome. Reason:This question shows you have put in some effort to learn the topic and seeking further clarification from the tutor.
- Bad What is coupling? - Such questions are discouraged. Reason: This question implies you haven’t done what you could to learn the topic in concern.
- Ask the lecturer: Failing all above, you can talk to the lecturer before/after the lecture, or email the lecturer.
Some technical problems can take a long time to resolve. Therefore, plan ahead and schedule your work much earlier than the deadline.
Some problems might not get resolved at all; while waiting for a solution, explore alternatives and workarounds.
Resources
- [lifehacker article] Google Tips and Tricks Every Student Should Know
- [Article] How To Ask Questions The Smart Way by Eric Steven Raymond